Step by Step OO Design
How to perform systematic OO design?
Learning outcomes
- We will learn about the following key OO Design principles
- Coupling
- Cohesion
- Reducing Coupling and Increasing Cohesion
- You will be able to:
- Perform the OO design of a simple case study
- Identify problems with your design
- Refactor the design to reduce coupling and increase cohesion
Consider the following user story:
The user needs a calculator with simple integer arithmetic operations. He wishes to input the numbers and the desired operation into the program, and expects a correct answer for this calculation. For quality reasons, the input and output should be easy to read out. S/he is not concerned with large numbers, and expects to use it for both positive and negative integers
Consider the following Java implementation
-
Where should this code go?
- Cohesion : Measure of how closely related all the responsibilities, data, and methods of a class are to each other.
- Coupling : Measure of how interconnected classes or subsystems are.

Increase cohesion and reduce coupling
Start by watching this video on Cohesion and Coupling
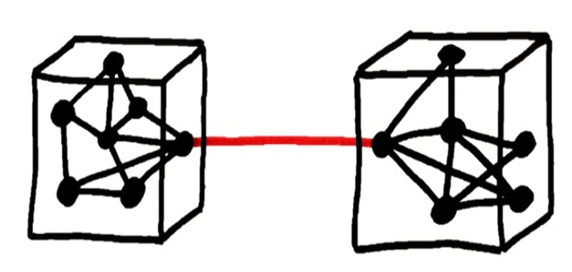
-
This is an well known OO design principle proposed by Larry Constantine
- The main idea is to develop reusable code that is immutable to changes of certain types of objects
- We will start by a step by step refactoring of this code as an OO program
The first OO Calculator

Is this code reusable?
-
Why? In order to increase understandability, reusability and maintainability of code.
-
Scenario 1: A company, which traditionally used workstations, may wish to adopt mobile platforms in future.
-
Scenario 2: A software product goes through several versions of improvement e.g., MS Office 97 – 2013
-
Scenario 3: A software company may re-use existing code base for a newer project.
-
Next we will do an ACP Exercise
- Identify the limitations in this code so that we can adapt this for
the above scenarios, specifically to:
- perform calculations in any alternative ways, such that other classes are not impacted by this change
- the dataInput class is reusable and could be used for other tasks in a new project
